Reimer-Tiemann Reaction
About Reimer-Tiemann Reaction
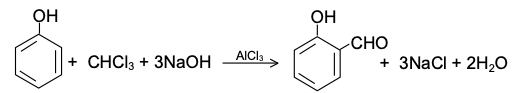
An alkaline solution of phenol is refluxed with chloroform at 60°C, distilling off the excess of chloroform and acidifying the residual liquid with sulphuric acid. As a result, o-hydroxy and p-;hydroxy benzaldehyde are formed, which are separated by steam-distillation.
Reaction Mechanism of Reimer-Tiemann Reaction
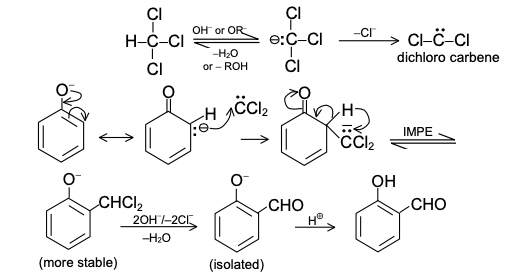
If ‘o’ both the o-positions are blocked, p-hydroxy benzaldehyde is the main product. With blocked p-position, o-hydroxy benzaldehyde and cyclohexadienones are formed.

Cyclohexadienone derivative remains unhydrolysed as it has a neopentylic system, which involves lot of steric crowding.
When phenol is refluxed with CCl4 in alkaline medium, salicylic acid is formed.
Example of Reimer-Tiemann Reaction

List of Name Reaction of Organic Chemistry consist of detail Reaction Mechanism of all name reactions of Organic Chemistry.
Recent Concepts
- Aldol condensation
- Arndt−Ester synthesis
- Baeyer−Villiger Oxidation
- Benzoin Condensation
- Beckmann Rearrangement
- Cannizzaro Reaction
- Clemmensen Reduction
- Claisen condensation
- Etard’s Reaction
- Friedel-Crafts alkylation
- Friedel Crafts Acylation
- Fries Rearrangement
- Gattermann-Koch Reaction
- Grignard Reagent
- Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky Reaction
- Hunsdieker reaction
- Hoffmann Bromamide Degradation
- Jones reagent
- Kolbes Reaction
- Knoevenagel Reaction



















